Please note, this page has been archived and is no longer being updated.
The Government’s new Clean Air Strategy could benefit from the work being done by an EU Interreg NWE-funded research programme, which is looking at potential uses for algae in mitigating and recycling waste which could cause pollution due to agricultural practices.
The Clean Air Strategy aims to reduce the amount of ammonia emissions from agriculture by 88%. These emissions, which are released when slurries, manures and nitrogen fertilisers come into contact with the air, can travel long distances and combine with other pollutants to form particulate matter which can be harmful to humans.
Storage and processing of large volumes of organic wastes through anaerobic digestion (AD) has been identified as a significant source of ammonia.
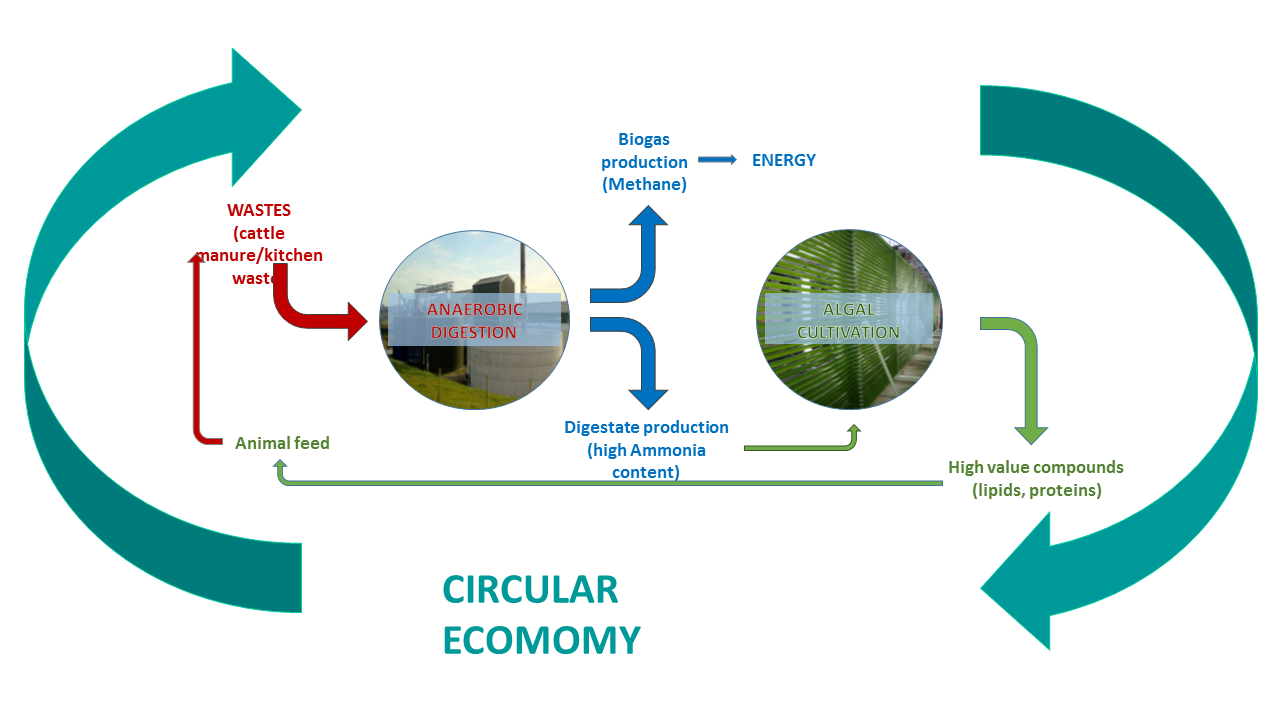
The ALG-AD project, which is being led by a team of academics based in Swansea University, takes excess waste nutrients produced from the AD of food and farm waste and uses it to cultivate algal biomass for animal feed and other value products.
The €5.5 million project involving 11 partners across North-West Europe is currently testing the technology at three pilot sites.
Dr Carole Llewellyn of Swansea University, (pictured), the scientist in charge of the project, said:
 “Technology being developed within the ALG-AD project could offer the farming community a sustainable and economical way of dealing with these emissions of ammonia.
“Technology being developed within the ALG-AD project could offer the farming community a sustainable and economical way of dealing with these emissions of ammonia.
By combining algal and AD technologies we are not only helping the farming community clean up the air; we are also creating useful by-products such as animal feed, which will add a revenue stream and close the resources loop through creating a circular economy.
Experiments using the nutrient rich digestate produced through anaerobic digestion to feed algae and create a usable biomass are about to get under way at three pilot sites across Europe. This biomass can be converted into animal feed and could provide a useful solution to the ammonia pollution problem.
The possibilities offered by this technology could solve a lot of problems around pollution being faced by the North West Europe area. And all of us working on ALG-AD are excited at the potential for the project to make a real and lasting difference.”
As part of the Clean Air Strategy support will be provided to farmers to invest in infrastructure and equipment to reduce their emissions.
Picture: diagram showing how the work contributes to a circular economy
- Tuesday 22 January 2019 14.37 GMT
- Tuesday 22 January 2019 15.37 GMT
- Public Relations Office
